and rated into four skill levels below. So for example, basic low skill levels for beginners will require basic fundamental knowledge of TeamSite. The higher the skill levels, the more tecnhnical knowledge of TeamSite is required to understand.
The skill levels are as follows:
Level 0: The Developer has no knowledge of or experience in the skill/knowledge area whatsoever.
Level 1: The Developer has a conceptual knowledge of the skill/knowledge area and has some limited commercial experience or may have experimented with the related concepts and/or supporting technologies in a non-commercial sense. The developer cannot apply this skill/knowledge area without direct supervision.
Level 2: The Developer is proficient in the skill/knowledge area with recent commercial experience in its application, can apply the skill/knowledge without direct supervision, but has insufficient experience/knowledge
to provide direction to others in the given area.
Level 3: The Developer can be considered an expert in the skill/knowledge area with considerable recent commercial experience in its application, with experience providing mentoring/guidance to others. The Developer has a detailed and broad understanding of the skill/knowledge area.
Note that each level described above subsumes all levels below it. Thus, in order for a TeamSite Developer to rate at Level 3, he or she must meet the criteria for Levels 1, 2 and 3.
The following area of TeamSite knowledge a TeamSite Developer need to obtain are broken down into each levels below:
Level 0
Introduction to Content Management System (CMS)
- Can describe the definition of TeamSite
- Can describe the features of TeamSite
- Can describe the definition of CMS
- Can describe the purpose of CMS
- Can describe the content development life cycle
- Cam describe the definition of an asset
Introduction to TeamSite Concept
- Can define TeamSite server architecture
- Can define TeamSite terminology like for example: i)
Content stores ii) Branches ii)Workareas iv) Edition and Versionin v)Can describe the definition and what are the roles in TeamSite vi)Metadata vii)Can log in to a TeamSite server - Can describe and demonstrate and use the features in each version of ContentCenter User Interface
Level 1
Editing files
- Can do simple and advance search for assets
- Can describe and use TeamSite VisualPrevew tool
- Can describe and use Local File Manager to edit files
- Can describe and perform basic file operations like copy, rename, delete, create, move/rename, import/export and modifying properties of a file
- Can view and set metadata
- Can describe and demonstrate checking in/out a file and able to perform merges
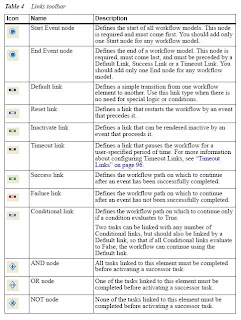
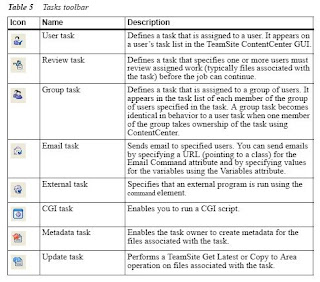
Introduction to Workflows
Can describe the workflow terminology use in TeamSite, like for example understand the following:
- Workflow
- Job specification
- Workflow Moder
- Workflow template
- Task
- Activation
- Transition
- Links
- Understand the difference between serial and parallel task
- Workflow events
Introduction to Forms Publisher
Can describe the forms publisher terminology use in TeamSite, like for example understand the following:
- Data Capture Templates (DCTs) / Data Capture Forms
- Data Content Records (DCRs)
- Presentation Template (PTs)
Level 2
Workflow Development
- Can describe and demonstrate how to configure and set up out of the box workflows templates and workflow models
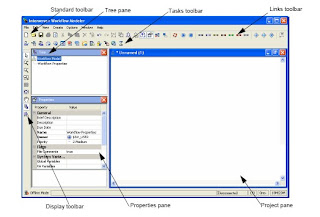
- Can describe and demonstrate how to design, implement and deploy a workflow using the Workflow Modeler Tool
- Can describe and demonstrate how to design, implement and deploy a customise workflow template using XML and Perl script
Form Publisher Development
- Can describe and demonstrate how to develop Data Catpure Forms
- Can describe and demonstrate how to develop Presentation Templates
- Can describe and demonstrate how to use APIs and Command Line with Data Capture Forms
OpenDeploy
- Can describe and demonstrate how to configure Open Deploy tool to deploy files to production server
Level 3
Advanced Workflow and Form Publisher Development
- Can describe and demonstrate executing external programs
- Can describe and demonstrate creating custom data source
- Can describe and demonstrate using external database with Data Catpure Forms
TeamSite Administration
- Can describe and install or upgrade TeamSite CMS, TeamSite Search, MetaTagger and Open Deploy
- Can describe and demonstrate the process of configuring and reindexing TeamSite Search
- Can demonstrate the maintenance process of creating, deleting, updating users, groups and roles in TeamSite
- Can describe and demonstrate the process of backing and restoring content store
- Can describe and demonstrate diagnosing error message with log files
- Can configure file virtualisation in TeamSite